Tired of replacing the food mixer every few years? Build your own & repair when needed.
Scanned from a 1970s Meccano manual. More here. Previously: How to make everything ourselves: open modular hardware.
Technology for Luddites
Tired of replacing the food mixer every few years? Build your own & repair when needed.
Scanned from a 1970s Meccano manual. More here. Previously: How to make everything ourselves: open modular hardware.
 I’m one of those people for whom it’s hard to get out of bed early, especially when I didn’t sleep enough. Setting an alarm clock makes little sense because I turn it off and go back to sleep. Setting multiple alarm clocks throughout the apartment might work, but it bothers the neighbours and I will still wake up too late. The only foolproof solution for me is a human alarm clock, but unfortunately this is not always available, or reliable.
I’m one of those people for whom it’s hard to get out of bed early, especially when I didn’t sleep enough. Setting an alarm clock makes little sense because I turn it off and go back to sleep. Setting multiple alarm clocks throughout the apartment might work, but it bothers the neighbours and I will still wake up too late. The only foolproof solution for me is a human alarm clock, but unfortunately this is not always available, or reliable.
Enter the professional human alarm clock, or knocker-up. Before the advent of reliable and affordable alarm clocks, British and Irish workers were woken up by a person who made sure they could get to work on time. The knocker-up used a baton to knock on clients’ doors or a long and light stick to reach windows on higher floors. Others used a pea-shooter.
 The knocker-up would not leave a client’s window until it was sure that the client had been awoken. People would agree verbally, in advance, or simply post a preferred time on doors or windows. There were large numbers of people carrying out the job, especially in larger industrial towns such as Manchester and London.
The knocker-up would not leave a client’s window until it was sure that the client had been awoken. People would agree verbally, in advance, or simply post a preferred time on doors or windows. There were large numbers of people carrying out the job, especially in larger industrial towns such as Manchester and London.
Generally the job was carried out by elderly men and women but sometimes police constables supplemented their pay by performing the task during early morning patrols. Larger factories and mills often employed their own knocker-ups to ensure labourers made it to work on time. The profession lasted at least until the late 1920s and in some regions until the 1950s. Bringing it back would not only make me reach early morning appointments on time. It would also create new employment, foster social cohesion, and save energy and resources.
Sources: 1 / 2 / 3 / 4. Thanks to Cynthia Hathaway.
 Controversy in the archery world.
Controversy in the archery world.
1. Badass Danish YouTuber Resurrects Stunning Archery Skills Dating Back Centuries
2. Did That Danish Archer Fool The Whole Internet?
Thanks to Edwin Gardner.
In the Ugandan slum of Wakaliga, a thriving film industry called Wakaliwood has emerged. Mixing elements of Western action flicks and Chinese Kung Fu movies with Ugandan culture, Wakaliwood’s movies have garnered a cult following not just in in Uganda, but all over the world. Vice headed to Wakaliga to spend a day on the set of the next Wakaliwood hit.
Thanks to Juan Nacho.
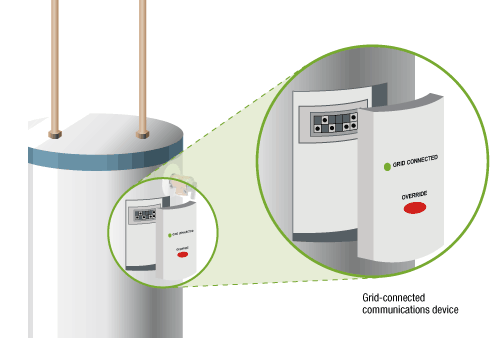 Grid-interactive water heaters (GIWHs) add bidirectional control to electric resistance water heaters, allowing a utility or third-party aggregator to rapidly toggle them off and on. This functionality turns a fleet of water heaters into a flexible energy-storage medium, capable of increasing and decreasing the load on the grid on a second-by-second basis.
Grid-interactive water heaters (GIWHs) add bidirectional control to electric resistance water heaters, allowing a utility or third-party aggregator to rapidly toggle them off and on. This functionality turns a fleet of water heaters into a flexible energy-storage medium, capable of increasing and decreasing the load on the grid on a second-by-second basis.
GIWHs are currently the least expensive form of energy storage available. Utilities can use fleets of grid-enabled water heaters for load shifting, demand response, arbitrage, ancillary services, or to respond to unexpected grid-stabilization events. Traditional dissemination of new water heater technology has been a painstakingly slow process, but water heater rental programs may greatly accelerate this process.
Read more: Battery Killers: How Water Heaters Have Evolved into Grid-Scale Energy-Storage Devices, David Podorson.
Related: How sustainable is stored sunlight?
“It turns out that digital devices and software are finely tuned to train us to pay attention to them, no matter what else we should be doing. The mechanism, borne out by recent neuroscience studies, is something like this:
With fMRIs, you can see the brain’s pleasure centres light up with activity when new emails arrive.
So, every new email you get gives you a little flood of dopamine. Every little flood of dopamine reinforces your brain’s memory that checking email gives a flood of dopamine. And our brains are programmed to seek out things that will give us little floods of dopamine. Further, these patterns of behaviour start creating neural pathways, so that they become unconscious habits: Work on something important, brain itch, check email, dopamine, refresh, dopamine, check Twitter, dopamine, back to work. Over and over, and each time the habit becomes more ingrained in the actual structures of our brains.”
Quoted from: Why Can’t We Read Anymore? The illustration was made by Luis Quiles — check out his work. Previously: Why the brain prefers to read on paper.
No Tech Magazine questions our blind faith in technological solutions. Mainly through links and quotes. Sister blog Low-tech Magazine brings original content.
Copyright © 2025 · Prose on Genesis Framework · WordPress · Log in