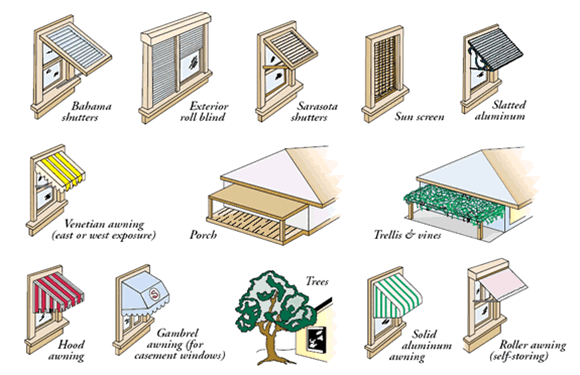
A house can be cooled in two ways. You can try to get rid of the incoming solar heat using air conditioning. Or you can try to prevent the sun from entering the house. The last option can be achieved by movable shading structures. The French house on the picture was built in 2009 by Karawitz Architecture.
Its shuttered bamboo skin can be used to keep the sun out in summer. The shutters can be opened in winter, exposing the large south-facing windows. The house, which stands in Bessancourt (not far from Paris), has no active heating or cooling system. Info + pictures. Via Build it solar. Thanks to Paul Nash.
Related: Window orientation and shading.